前言 组件仓库链接: 组件仓库
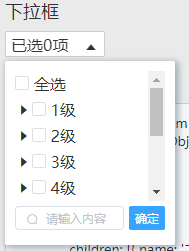
组件效果图:
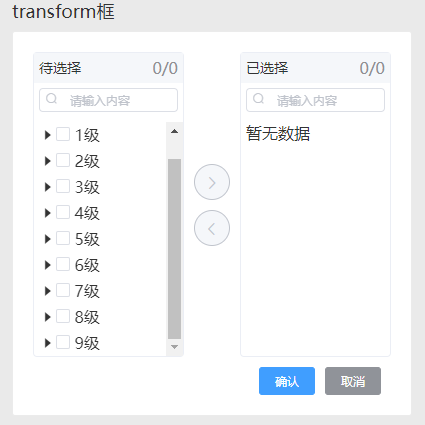
组件应用:
因为工作需要,需要处理一个10w+数据量的transfer,所以将公司原先组件进行重构和升级。
前提基础学习:GUI渲染时机、常见的超长列表渲染
超长单列表的渲染以及优化
再1的基础上,兼容分级列表
选择器transfer的构造
封装成插件,发布到npm上(to-do-list)
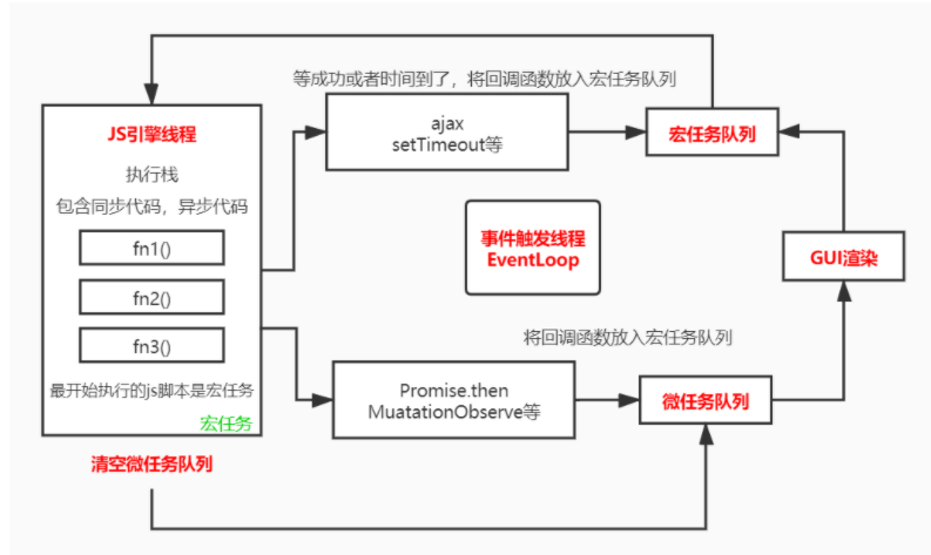
1. 前提基础学习 a. GUI渲染时机 首先了解这个,要先了解js引擎是怎么工作的。
js引擎是单核引擎,也就是说,js引擎只能开一条线程来处理进程。我们可以把这条线程,看成执行栈 ,里面会顺序推入要执行的代码块(比如函数),执行这块代码再去处理下块代码。
那遇到异步任务怎么实现异步呢,关于这个可以参考下面流程图:
①首先可以将一个js脚本看成一个宏任务,然后从上至下依次执行代码,遇到异步任务。②将异步任务分类,如果是微任务(如Promsie)就将微任务的回调函数放入微任务队列,如果是宏任务,就等宏任务成功或者时间到了(此时js引擎会将这个任务挂起,继续执行当前的同步代码),将成功回调放入宏任务队列。③当前同步代码全部执行完毕后,js引擎会去触发EventLoop轮询处理线程,先去看当前微任务队列是有有任务,若有任务,从队头任务开始执行,④等当前微任务队列清空后,浏览器会进行一次GUI渲染 ,⑤然后会去取一个宏任务放到执行栈,开始执行同步代码,遇到异步任务重复②
以上便是EventLoop的原理。得出结论:GUI渲染是在当前任务清空之后,执行下一个宏任务之前,进行的!
1 <div id ="container" > </div >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 let total = 100000 ;let timer = Date .now()for (let i = 0 ;i < total; i++>){let li = document .createElement('li' )document .getElementById('container' ).appendChild(li)console .log(Date .now() - timer)
这段函数的本意是要计算total个li渲染到页面花了多少时间,但运行后会发现,输出的时间很短,但页面还未渲染完成100000个li。原因就是因为js引擎会将当前所有同步代码执行后,才会进行GUI渲染。对于js引擎来说,遍历100000次很轻松,但渲染100000个li却没有那么友好,因此会有一段白屏时间。
那我们如何去计算函数从执行到页面渲染完毕的时间呢?可以在输出语句加上个定时器(宏任务),在执行定时器的之前,GUI渲染已经完成
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 let total = 100000 ;let timer = Date .now()for (let i = 0 ;i < total; i++>){let li = document .createElement('li' )document .getElementById('container' ).appendChild(li)() =>console .log(Date .now() - timer)0 )
b. 如何处理超长列表渲染
分片:根据数据大小,每次加载固定的数量。但有个明显缺点,加载越多,页面上累积的dom元素会很多,对性能不友好
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 let total = 10000 ;let index = 0 ;let id = 0 ;const NUM = 20 function load (if (index < total){() =>let fragment = document .createDocumentFragment();for (let i = 0 ;i<NUM;i++){ let li = document .createElement('li' )document .getElementById('container' ).appendChild(li)
虚拟列表优化,只渲染当前的可视区(可以参考github上一个很成熟的vue插件:vue-virtual-scroll-list)
原理 :把列表当成一个数组,用开始指针和结束指针去决定可视区域的数据展示,当滚动条滑动的时候,去算滑过多少个了,指针也跟着移动位置,去指向应该展示的数据位置;如果列表每项不定高的话,还需要刷新每项的高度和滚动条的高度,这部分比较复杂。
具体实现看第二部分
2. 超长单列表的渲染以及优化 思路大概是:
不管列表多长,我需要只显示可视区域有数据
告诉我的列表每一项多高(itemH)和多少条数据(datas) ==> 滚动条的高度
可设定显示多少条(showNum)
可设定是否不定高加载
列表结构设计 :
主容器:可滚动的盒子,监听滚动事件。设置相对定位和overflow:scroll
内层虚拟列表:设置相对定位,用于撑开主容器,用于展示数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 <div class ="viewport" ref ="view" @scroll ="handleScroll" > <div class ="virtual-list" ref ="virtualList" :style ="{paddingTop:`${offset}px`,lineHeight:`${itemH}px`}" > <div v-for ="(item,index) in virtualList" class ="item" :key ="item.key" ref ="item" > <slot :item ="item" > </slot > </div > </div > </div > <style lang ='stylus' scoped > .viewport .virtual-list .item </style >
初始化:mouted阶段
主容器的高度 = itemH * showNum
虚拟列表的真实高度 = itemH * datas.length
end = start + showNum
虚拟列表数据:virtualList = datas.slice(start,end),切割真实列表来形成
滚动条监听
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 handleScroll() {let scrollTop = this .$refs.view.scrollTop;this .start = Math .floor(scrollTop / this .itemH); this .end = this .start + this .showNum;this .offset = this .start * this .itemH;
到这,一个最基础的虚拟列表加载就完成了。但还有很多细节要处理。
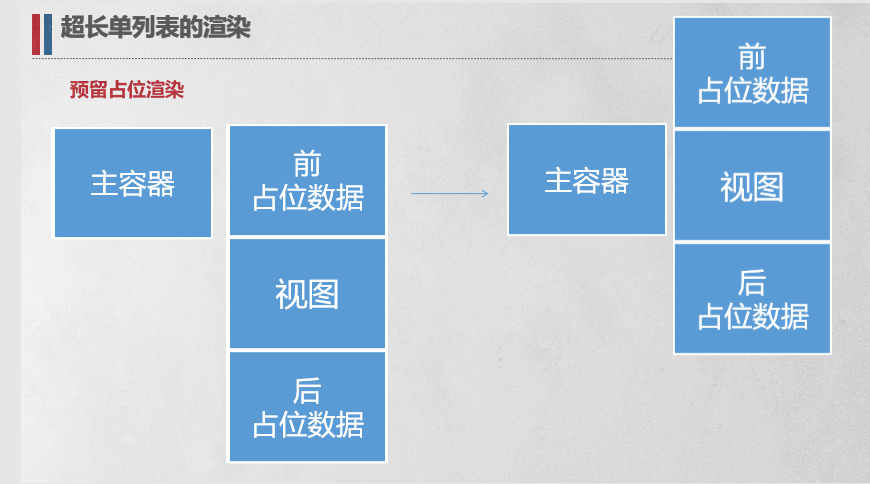
预留占位渲染 前后 加上一品列表(数量也可以自定义)。可以通过将前后指针分别前后移动,增加虚拟列表渲染范围,同时需要将虚拟列表的视口取在中间段。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 return Math .min(this .start, this .showNum);return Math .min(this .datas.length - this .end, this .showNum);this .datas.slice(this .start - this .prevCount, this .end + this .nextCount)
优化滚动节流:借助lodash1 2 3 4 5 import throttle from 'lodash/throttle' this .scrollFn = throttle(this .handleScroll,200 ,{leading;false })
不定高加载设计
。。。 待补充
3. 超长多级列表的渲染 常见的超长列表渲染貌似都是考虑单列表(也就是一个列表),因为工作业务上的需求,我决定优化一下,设计成可以兼容二级列表。假设传入的是Map对象,即为二级列表
需要哪些变量来控制
foldFlag: 数组,值为true和false。控制展开哪个二级列表,只能展开一个二级列表(数组值只有一个true,其它为false)unFoldIndex: Number,保存当前展开的一级列表id,没有展开则为null
html结构上兼容
通过v-if和v-else来决定显示哪种列表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 <div class ="viewport" ref ="view" @scroll ="scrolFn" :style ="{maxWidth:setMaxWidth}" > <div class ="virtual-list" ref ="virtualList" :style ="{paddingTop:`${offset}px`,lineHeight:`${itemH}px`}" > <div class ="item" v-for ="(item,index) in virtualList" :key ="item[0]+'-'+index" > <div class ="single-list" v-if ="Array.isArray(datas)" :style ="{height:`${itemH}px`}" > <slot name ="singleList" :item ="item" > </slot > </div > <div class ="main-list" :style ="{height:`${itemH}px`}" @click ="toggleFold(index,item)" v-else > <span style ="display:inline-block;width:12px" > <span class ="el-icon-caret-right" :style ="{transform: foldFlag[index]?'rotate(90deg)':'rotate(0deg)'}" v-show ="datas && datas.get(item[0])['children'].length>0" > </span > </span > <slot name ="main" :main ="item[0]" > {{item[0]}}</slot > </div > <ul class ="fold_tree" style ="padding-left:30px;list-style: none;margin:0;" v-if ="!Array.isArray(datas)&&foldFlag[index]&&item[1]['children'].length>0" > <li style ="white-space: nowrap;" v-for ="(child,idx) in item[1]['children'].slice()" :key ="road[label]+'-'+road[nodekey]" > <slot name ="sub" :sub ="child" > </slot > </li > </ul > </div > <div v-if ="datas.length == 0||datas.size==0" > 暂无数据</div > </div > </div >
初始化阶段
默认不展开二级菜单,则初始化只需展示所有的一级菜单即可
滚动条长度 = this.datas.size * this.itemH
start = 0
end = start + showNum > this.datas.size ? showNum :datas.size;
虚拟列表数据:当前没有展开,便返回整个datas
展开二级列表设计
思路为:点击的时候去判断:以下展开情况,并计算各种情况的真实高度
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 toggleFold(index, item) {let scrollH;if (this .unFoldIndex === index) {this .$set (this.foldFlag, index, !this.foldFlag[index]);this .$set (this.foldFlag, index, true);get (item[0])["children"].length);this .$set (this.foldFlag, this.unFoldIndex, false);set (this.foldFlag, index, true);get (item[0])["children"].length);
虚拟列表的截取
思路:先判断有无展开,无展开便展示一级菜单;有展开便去获取当前展开的一级菜单的id和二级项,然后在二级项去截取。向后占位也要判断是否有展开
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 virtualList() {if (this .datas) {if (Array .isArray(this .datas)) {return this .datas.slice(this .start - this .prevCount,this .end + this .nextCountelse {if (this .unFoldIndex === null ) {return this .datas;else {let data = new Map ();this .datas.forEach((road, name ) => {let obj = { children : [], id : road.id };this .label] = road[this .label];this .nodekey] = road[this .nodekey];let key = [...this.datas][this .unFoldIndex][0 ];let roadArr = [...this.datas][this .unFoldIndex][1 ]["children" ].slice(this .start - this .prevCount,this .end + this .nextCountlet newObj = data.get(key);"children" ] = roadArr;return data;if (Array .isArray(this .datas)) {return Math .min(this .datas.length - this .end, this .showNum);else {if (this .unFoldIndex === null ) {return Math .min(this .datas.size - this .end, this .showNum);else {let data = [...this.datas][this .unFoldIndex][1 ];return Math .min(data.length - this .end, this .showNum);
滚动监听
思路:如果有展开,并且滚动距离已经超过当前要展开的一级列表上面菜单的总高度,便去更改start,end,offset
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 handleScroll() {let scrollTop = this .$refs.view.scrollTop;if (Array .isArray(this .datas)) {this .start = Math .floor(scrollTop / this .itemH); this .end = this .start + this .showNum;this .offset = this .start * this .itemH - this .prevCount * this .itemH;else {if (this .unFoldIndex != null ) {if (scrollTop > (this .unFoldIndex + 2 ) * this .itemH) {this .start = Math .floor(this .unFoldIndex + 1 ) * this .itemH) / this .itemHthis .offset = this .start * this .itemH - this .prevCount * this .itemH;else {this .start = 0 ;this .offset = 0 ;this .end = this .start + this .showNum;
勾选功能的设计
引入勾选功能,可以在加上一个是否开启可以勾选的变量。思路是:用一个集合new Set()来保存已选中的item,每条的勾选框的v-model用是否存在勾选集合中来显示。
全选:判断当前是否勾选了->若勾选了,取消勾选,并set.clear(),清空集合;->若没有勾选,全选,并把所有一级菜单和二级菜单全部add
一级全选:判断当前是否勾选了-> 若勾选了,取消当前一级勾选和全选和当前子集 -> 若没有勾选,勾选一级菜单和当前子集,判断当前一级菜单是否全部勾选了(arr.every(()=>{}))
二级单条勾选:判断当前是否勾选了 -> 若勾选了,取消勾选自己和当前所在一级勾选和全选 -> 若没有勾选,勾选自己,并且判断当前所在一级菜单是否全选了和是否全选了
过滤搜索功能的设计
思路是先给数据打上拼音标识,比如网格001(wangge001),国道s108(guodaos108),然后再输入的时候,将输入值转成拼音,在所有数据的拼音标识遍历,若包含在里面便返回
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 if (Array .isArray(this .datas)) {() =>this .datas = this .datas.map("py" ] = this .setPinyinConvert(e[this .label]);return e;0 );else {() =>this .datas.forEach((val, key ) => {if (val["children" ].length > 0 ) {"children" ] = val["children" ].map(e =>"py" ] = this .Pinyin.convertPinyin(e[this .label]);return e;this .datas.set(key, val);else {"py" ] = this .Pinyin.convertPinyin(val[this .label]);this .datas.set(key, val);0 );let results = [];if (searchVal) {let py = this .Pinyin.convertPinyin(searchVal.toLowerCase());if (!Array .isArray(this [dataName])) {this [dataName].forEach((val, key ) => {if (val["children" ].length > 0 ) {"children" ].filter(e =>"parentKey" ] = key;return (e["py" ].toLowerCase().indexOf(py) > -1 );else {if (val["py" ].toLowerCase().indexOf(py) > -1 ) {else {this [dataName].forEach(item =>if (item["py" ].toLowerCase().indexOf(py) > -1 ) {else {this [dataName];this [resultMapName] = results;